Background:
Extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL) is a highly malignant non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), which has no standard treatment available for this subgroup. Conventional treatment approaches (L-asparaginase- or pegaspargase-based regimen) failed to achieve long-term clinical benefit. The prognosis of advanced ENKTL is poor even in newly diagnosed patients (pts) due to a high relapse rate of 70%. Substantial evidences indicate that anti-programmed death-1 (PD-1) monoclonal antibody has achieved promising efficacy in refractory or relapsed ENKTL (Kwong et al. Blood 2017, Li et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology 2018, Tao et al. JCO 2020). Results from our retrospective study demonstrated a manageable tolerability profile and favorable anti-tumor activity of anti-PD-1 antibody combined with P-GEMOX (pegaspargase, gemcitabine and oxaliplatin) regimen in untreated advanced ENKTL pts (unpublished data). Therefore, a phase 2 trial (NCT04127227) was initiated to evaluate safety and efficacy of sintilimab (a fully human anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody) plus P-GEMOX regimen as first-line therapy in advanced ENKTL pts. Here, we report the preliminary results of the study.
Methods:
This study enrolled adult pts with untreated pathologically confirmed ENKTL with at least one measurable lesion. A sample size of 34 pts was preplanned, with 6 pts recruited for a safety run-in cohort. Pts received six 21-day cycles of sintilimab 200 mg, pegaspargase 2000 U/m2 (day 1), gemcitabine 1g/m2 (days 1 and 8), and oxaliplatin 130 mg/m2 (day 1), followed by sintilimab 200 mg maintenance every 3 weeks for up to 2 years or until documented confirmed disease progression or intolerable toxicity. Of the run-in cohort, preliminary safety and dose-limiting toxicity (DLTs) analyses were performed in the first cycle of treatment, primary endpoints were safety and tolerability of the combination therapy. DLTs were defined as grade 4 neutropenia that does not resolve to grade </= 2 within 7 days; grade 4 thrombocytopenia that does not resolve within 7 days; any grade >/= 3 nonhematologic toxicity lasting for more than 7 days, and any treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) that results in a delay for more than 14 days of initiating cycle 2. Of the entire cohort, primary endpoints were complete response (CR) rate and objective response rate (ORR), secondary endpoints included overall survival, progression-free survival, and safety. TRAEs were accessed according to CTCAE 5.0. Response assessments were performed using PET/CT or MRI scans every 6 weeks of the combined treatment and every 3 months of maintenance treatment.
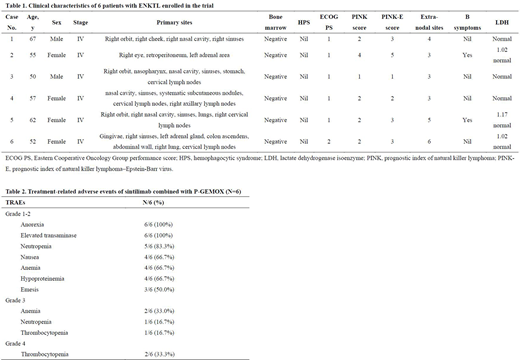
Results: Six pts with untreated ENKTL were enrolled between Sept 19, 2019 and Jul 26, 2020. Median age was 56 years (range 52-67). All pts were found to be found to be positive for EBV encoded RNA (EBER) by in situ hybridization. Clinical characteristics of all pts are listed in Table 1. Median number of treatment cycles was 7 (range 4-11). At data cut-off, 5 pts completed 6 cycles of combination therapy and entered the maintenance phase (median: 1, range 1-5). No DLTs were observed. The majority of TRAEs were reported during the first two cycles of the combination treatment. The most common TRAEs were anorexia (6/6, 100%), elevated transaminase (6/6, 100%), neutropenia (5/6, 3.3%), nausea (4/6, 66.7%), anemia (4/6, 66.7%), hypoproteinemia (4/6, 66.7%), vomiting (3/6, 50.0%) and thrombocytopenia (3/6, 33.3%). Grade 3/4 TRAEs occurred in 4 (66.7%) pts, including thrombocytopenia (1/6, 16.7%), anemia (2/6, 33.0%), and neutropenia (1/6, 16.7%). Details of all-grade TRAEs are listed in Table 2. All the TRAEs were manageable and reversible. No immune-related (ir) AE or treatment-related death was observed. Of the 6 pts received response assessments, ORR was 100% (6/6) and CR rate was 33.3% (2/6). After a median follow-up of 7.8 months, 5 pts were still on the planned treatment and maintained favorable outcomes. The updated data will be reported at the ASH conference.
Conclusions:
Sintilimab plus P-GEMOX regimen demonstrated manageable safety profile and promising anti-tumor activity in pts with untreated advanced ENKTL. The preliminary safety and efficacy profile of combination therapy support further study and the exploration of effective biomarkers for predicting the treatment response is under way.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Sintilimab is medication that is indicated for the treatment of relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin's lymphoma after failure of at least second-line systemic chemotherapy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.